Understanding Google Search Console Errors
Have you ever logged into Google Search Console (GSC) only to be met with a list of errors that seem overwhelming? You're not alone. Understanding and resolving these errors is essential for optimizing your website’s performance and maintaining strong rankings on search engine results pages (SERPs). In this guide, we’ll break down the most common GSC errors, explain their impact, and provide actionable steps to resolve them effectively.
At Searchlight Digital, we have worked with over 500 websites and leverage Google Search Console as a key tool for ensuring that a site’s health is in good standing, track and measure performance over time, and leverage customized data for each client’s site to continuously improve performance.
Table of Contents
Crawl Errors: Identifying and Fixing Access Issues
404 (Not Found) Errors
500 (Server Errors)
DNS Errors
Soft 404 Errors
How to Fix Crawl Errors
Mobile Usability Issues: Optimizing for a Mobile-First World
Content Wider Than Screen
Clickable Elements Too Close Together
Viewport Not Configured
How to Fix Mobile Usability Issues
Structured Data Errors: Enhancing Search Appearance
Common Structured Data Errors
How to Fix Structured Data Errors
Index Coverage Issues: Ensuring Proper Indexing
Excluded Pages
Duplicate Content
Crawled – Currently Not Indexed
How to Fix Index Coverage Issues
Common Indexing Errors in Google Search Console and How to Fix Them
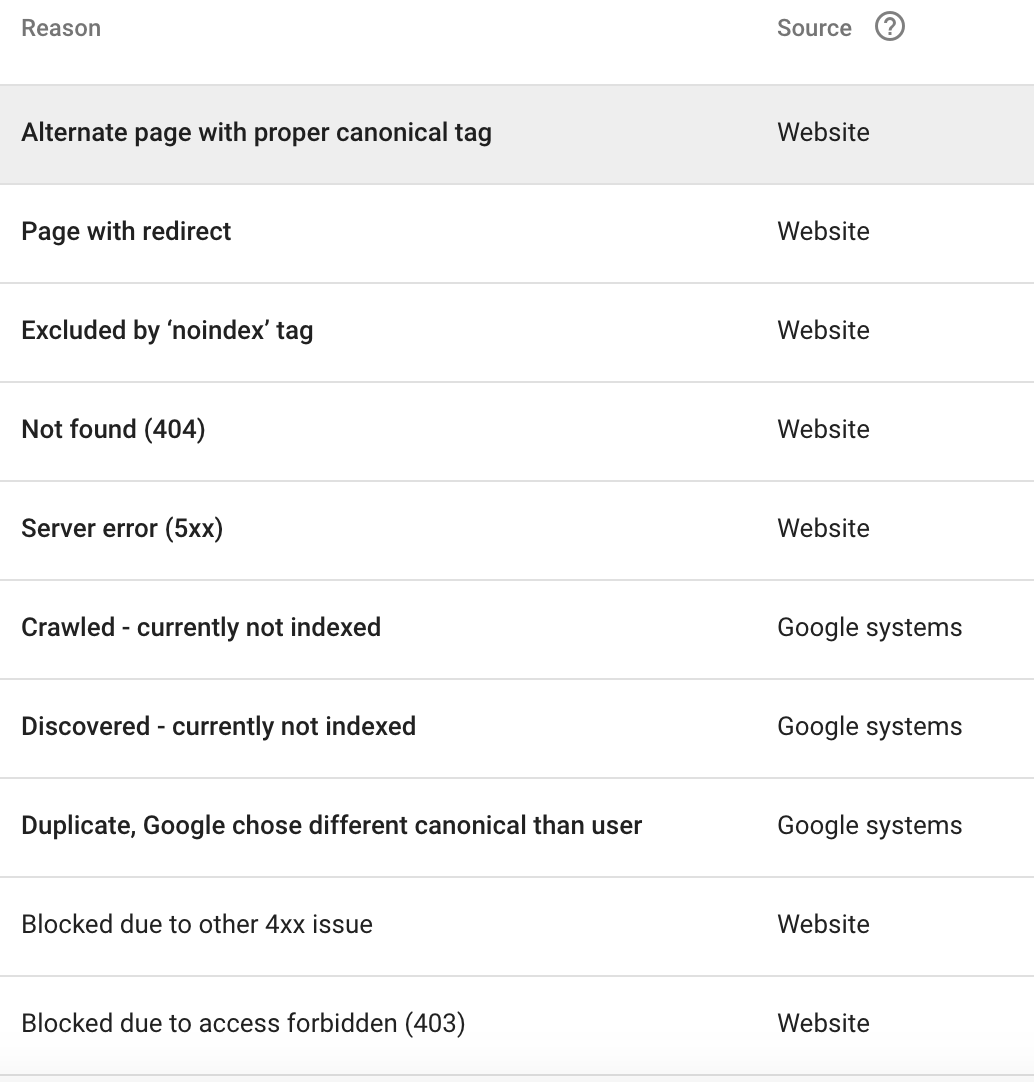
Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag
Page with Redirect
Excluded by ‘noindex’ Tag
Not Found (404)
Server Error (5xx)
Crawled – Currently Not Indexed
Discovered – Currently Not Indexed
Duplicate, Google Chose Different Canonical than User
Blocked Due to Other 4xx Issue
Blocked Due to Access Forbidden (403)
Security Issues: Protecting Your Website from Penalties
How to Fix Security Issues
Leverage GSC for Continuous Improvement
Key Takeaways
Crawl Errors: Identifying and Fixing Access Issues
Crawl errors occur when Googlebot encounters problems while navigating your website. These issues prevent search engines from properly indexing your content, which can negatively impact your rankings. Common crawl errors include:
404 (Not Found) Errors: These occur when a page has been deleted or its URL has changed without a proper redirect. Broken links within your website or from external sources can also trigger 404 errors.
500 (Server Errors): These indicate that the server is unable to fulfill the request due to an internal issue, such as a misconfigured server, a database error, or resource overload.
DNS Errors: These arise when Google cannot communicate with your website due to a misconfigured DNS setup or downtime.
Soft 404 Errors: These happen when a page returns a ‘200 OK’ response instead of a proper ‘404 Not Found’ message, misleading search engines into indexing empty or non-existent pages.
How to Fix Crawl Errors:
Use GSC’s Crawl Error Report to identify problematic URLs.
Implement 301 redirects for pages that have been moved or replaced.
Ensure your server is properly configured and can handle increased traffic loads.
Use tools like Google’s URL Inspection Tool to check if Googlebot can access a page correctly.
Mobile Usability Issues: Optimizing for a Mobile-First World
Since Google’s transition to mobile-first indexing, ensuring your site is mobile-friendly is no longer optional. Mobile usability issues can harm your rankings and user experience. Common issues include:
Content Wider Than Screen: This occurs when your content does not scale properly for mobile devices, causing horizontal scrolling.
Clickable Elements Too Close Together: Small or crowded buttons and links can make navigation frustrating for mobile users.
Viewport Not Configured: This means your site lacks a responsive viewport meta tag, leading to improper scaling on different devices.
How to Fix Mobile Usability Issues:
Use GSC’s Mobile Usability Report to detect and resolve issues.
Implement responsive design using CSS media queries.
Increase spacing between clickable elements to enhance usability.
Ensure your viewport meta tag is set correctly (
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">).
Structured Data Errors: Enhancing Search Appearance
Structured data helps search engines understand the context of your web pages, improving the likelihood of appearing as rich snippets in search results. Errors in structured data markup can prevent Google from properly interpreting your content, leading to missed SEO opportunities.
Common Structured Data Errors:
Incorrect Schema Markup: Missing required properties or using outdated schema types.
Invalid JSON-LD Format: Syntax errors in your structured data code.
Mismatched Content: When structured data does not align with on-page content, Google may ignore it.
How to Fix Structured Data Errors:
Use Google’s Rich Results Test and Schema Markup Validator to check for errors.
Ensure your schema is correctly implemented by referring to Google’s Structured Data Guidelines.
Regularly validate and update your structured data as new schema types emerge.
Index Coverage Issues: Ensuring Proper Indexing
Index coverage issues indicate that Google is having trouble indexing certain pages on your site. These errors can result from:
Excluded Pages: Pages intentionally or unintentionally blocked by a
robots.txtfile,noindextags, or canonical tags.Duplicate Content: Google may choose not to index certain pages due to perceived duplication.
Crawled – Currently Not Indexed: Google has crawled the page but decided not to index it, possibly due to thin content or low quality.
Common Indexing Errors in Google Search Console and How to Fix Them
Google Search Console provides valuable insights into how Google indexes your website. However, various indexing errors can prevent your pages from appearing in search results. Below are the most common indexing issues, their causes, and how to fix them.
1. Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag
What It Means: Google has found a duplicate page but is indexing the preferred (canonical) version instead.
Fix: No action is needed unless Google is choosing the wrong canonical URL. Ensure the canonical tag on the preferred page is correctly implemented.
2. Page with Redirect
What It Means: The page is redirected to another URL, and thus Google does not index it.
Fix: If the redirect is intentional, no action is required. If unintended, review your redirects using GSC’s URL Inspection Tool and correct any misconfigurations.
3. Excluded by ‘noindex’ Tag
What It Means: The page contains a
noindexmeta tag, instructing Google not to index it.Fix: If you want the page indexed, remove the
noindextag and request reindexing in Google Search Console.
4. Not Found (404)
What It Means: The page is missing, leading to a 404 error.
Fix: Either restore the missing page, set up a 301 redirect to a relevant page, or leave the 404 if the content is permanently removed and unnecessary.
5. Server Error (5xx)
What It Means: Google attempted to crawl the page but encountered a server-side error.
Fix: Check your server logs to diagnose issues. Ensure the server is not overloaded and all hosting settings are correctly configured.
6. Crawled – Currently Not Indexed
What It Means: Google has crawled the page but decided not to index it, often due to low-quality content or duplication.
Fix: Improve content quality by making it unique, valuable, and well-structured. Use Google’s URL Inspection Tool to check for indexing eligibility.
7. Discovered – Currently Not Indexed
What It Means: Google has found the page but has not crawled it yet. This usually happens due to crawl budget limitations.
Fix: Ensure the page has internal links and is part of your XML sitemap. If the issue persists, request indexing through Google Search Console.
8. Duplicate, Google Chose Different Canonical than User
What It Means: Google has ignored the user-defined canonical URL and indexed a different version.
Fix: Review the canonical tag implementation and check for conflicting signals (e.g., inconsistent internal links or sitemap entries).
9. Blocked Due to Other 4xx Issue
What It Means: The page is inaccessible due to a client-side error other than 404 or 403.
Fix: Use Google’s URL Inspection Tool to identify the exact issue. Check your CMS settings and web server configurations for restrictions.
10. Blocked Due to Access Forbidden (403)
What It Means: The server is blocking Googlebot from accessing the page, likely due to permission settings.
Fix: Review server permissions, check for firewall rules blocking Googlebot, and update
.htaccessor security settings if needed.
How to Fix Index Coverage Issues:
Review GSC’s Index Coverage Report to identify affected pages.
Ensure important pages are not blocked by
robots.txtornoindexdirectives.Improve content quality to provide unique and valuable information.
Use canonical tags properly to avoid unintentional duplicate content issues.
Security Issues: Protecting Your Website from Penalties
Security threats such as malware, phishing attacks, and hacked content can damage your site’s reputation and lead to ranking penalties. Google Search Console flags security issues to help protect users and maintain trust.
How to Fix Security Issues:
Check GSC’s Security Issues Report for flagged threats.
Use Google’s Safe Browsing Tool to verify your site’s status.
Remove malware or malicious code by working with your web hosting provider.
Implement SSL certificates (HTTPS) to encrypt user data and improve security.
Keep your CMS, plugins, and scripts updated to prevent vulnerabilities.
Leverage GSC for Continuous Improvement
Google Search Console is a powerful tool for monitoring and optimizing your website’s health. By proactively identifying and resolving errors, you can enhance your site’s search visibility, user experience, and overall SEO performance.
Key Takeaways:
Regularly check GSC reports to stay ahead of potential SEO issues.
Prioritize mobile usability for optimal user experience and rankings.
Implement structured data correctly to increase rich snippet opportunities.
Address index coverage issues to ensure your pages appear in search results.
Strengthen website security to avoid penalties and protect user trust.
By integrating GSC into your ongoing SEO strategy, you can ensure your site remains competitive, user-friendly, and primed for success in Google search rankings.
Ready to tackle GSC errors and elevate your website's search presence? Contact Searchlight Digital today for expert SEO guidance and support. Let us help you navigate the complexities of Google Search Console and optimize your website for success. Schedule a free consultation with our team and take the first step towards unlocking your site's full potential in search.